Compare commits
2 Commits
6b4d03876e
...
1e29344455
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1e29344455 | |||
| b21ea8ffef |
BIN
doc/图像分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-27-02.mp4
Normal file
BIN
doc/图像分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-27-02.mp4
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
BIN
doc/图像分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-40-16.png
Normal file
BIN
doc/图像分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-40-16.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 149 KiB |
93
doc/图像分类/README.md
Normal file
93
doc/图像分类/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
## 图像分类
|
||||
> 核心概念: 迁移学习、分类模型、图像识别、可视化
|
||||
### 图像分类模型怎么“看”世界的?
|
||||
想象一下,你刚出生时,并不知道什么是“猫”,什么是“狗”。但随着你慢慢长大,爸爸妈妈会指着图片告诉你:“看,这是猫!喵呜~” “这是狗!汪汪!” 慢慢地,你就能区分它们了。
|
||||
|
||||
AI也是一样! 它需要大量的图片来学习。分类模型就像一个“图像辨认大师”,它的任务就是学会区分不同类别的图片,比如猫、狗、汽车、飞机等等。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 尝试一下!
|
||||
|
||||
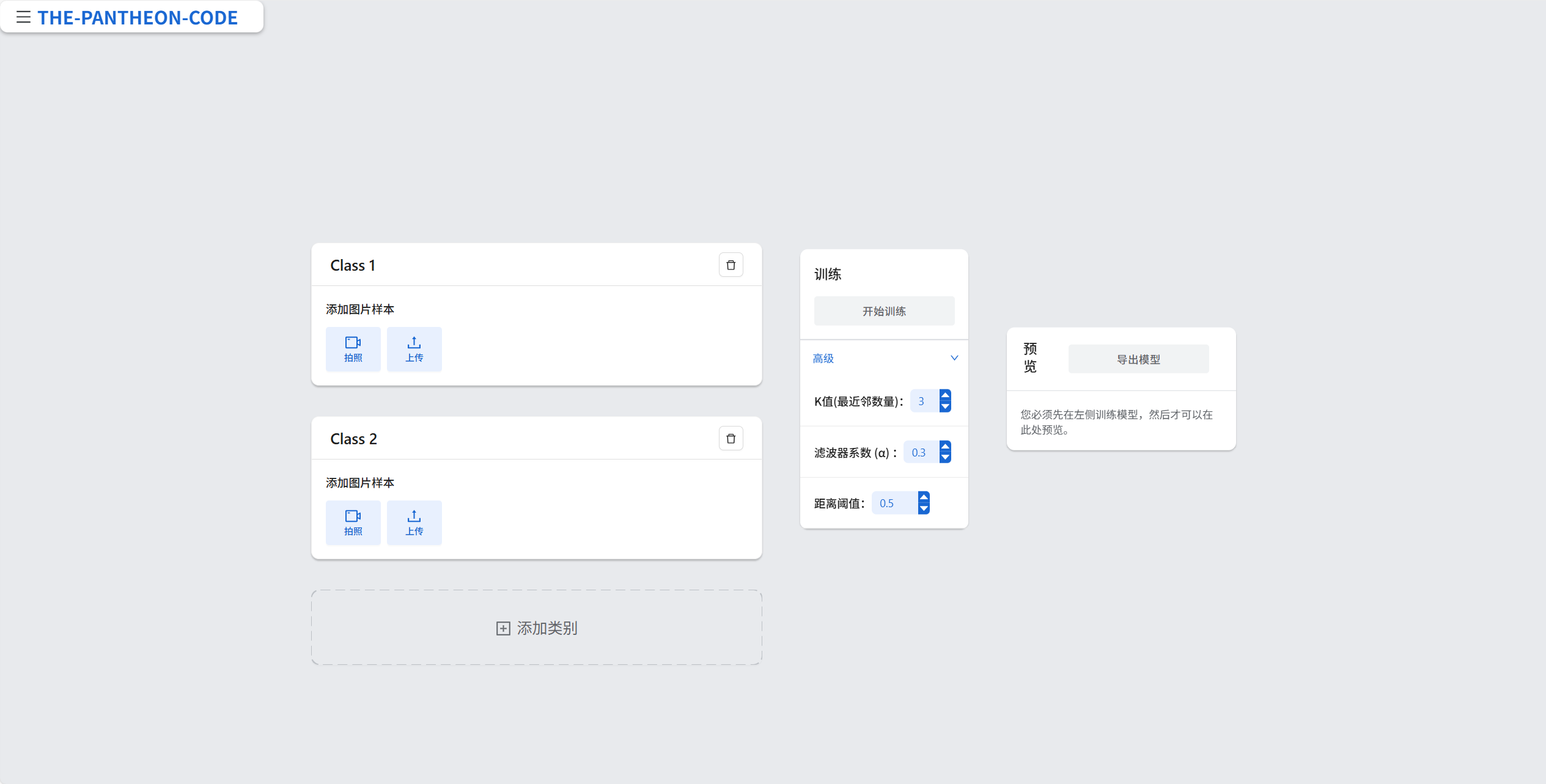
|
||||
|
||||
+ 上传你的训练图片--给AI“上课”!
|
||||
|
||||
比如,如果你想让AI区分“苹果”和“香蕉”,你就需要在“苹果”这个类别下上传一些苹果的图片,在“香蕉”这个类别下上传一些香蕉的图片。为每个类别上传图片即可。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,尝试上传不同角度、不同光线、不同大小的苹果图片。确保AI能“看到”不同特征。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
+ 点击“训练模型”--让AI“学习”!
|
||||
|
||||
模型便会从你提供的不同样本中学习到特征,这个过程可能只需要几秒钟甚至更短。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
+ 测试你的AI——看看它学得怎么样!
|
||||
|
||||
现在是检验成果的时候了!上传一张新的图片,比如你没给AI看过的苹果或香蕉。
|
||||
|
||||
AI会立刻告诉你,它觉得这张图片是“苹果”还是“香蕉”,还会告诉你它有多大的把握(比如“98%确定是苹果”)。
|
||||
|
||||
哇塞! 是不是超酷?你的AI现在也能“看懂”图片了!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<video controls src="https://goood-space-assets.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/public/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-27-02.mp4" title="Title"></video>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
玩了几轮之后,你可能会有更多的问题:
|
||||
|
||||
+ 如果AI判断错了怎么办?
|
||||
|
||||
这可能意味着你需要给AI更多的图片,或者图片不够清晰、不够多样。
|
||||
|
||||
+ 图片数量越多越好吗?
|
||||
|
||||
思考题: 如果我只给AI看一张图片,它能学会吗?
|
||||
|
||||
+ AI还能做些什么?
|
||||
|
||||
展望: 你觉得街上的无人驾驶汽车是怎么“看”路况的?医生是怎么通过AI分析X光片的?这些都离不开图像识别技术!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 小秘密:AI学习的“加速器”——迁移学习!
|
||||
|
||||
你可能会好奇:“哇,让AI学这么多东西,肯定要花好久好久吧?”
|
||||
|
||||
如果你让AI从零开始学习——就像你从出生开始学所有东西一样——那确实会非常非常慢,需要成百上千张图片来学习每个类别,并且用专业的机器训练数小时甚至数天。这是一个既耗时又昂贵的过程,不是我们普通人能轻松尝试的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在AI的世界里,有一个类似的“加速器”,它叫迁移学习(Transfer Learning)。
|
||||
|
||||
想象一下,我们已经有一个超级聪明的AI,它已经“看”了几百万张图片,并且学会了如何识别图像中各种基础的形状、颜色、纹理(就像它已经学会了平衡能力)。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们想让这个AI学会一个新任务,比如区分“蛋糕”和“披萨”。如果让它从零开始学习,会很慢。
|
||||
|
||||
“借用”超级大脑: 想象一下,我们已经有一个超级聪明的AI“教授”,它已经“看”了几百万张图片,并且学会了如何识别图像中各种基础的形状、颜色、纹理、边缘特征(就像它已经学会了平衡能力,更像是学会了识别世间万物的“零部件”)。
|
||||
|
||||
我们的秘诀: 这个“教授”就是预训练模型,比如我们用的 MobileNet!它已经学习过上千种物品的特征,能准确地识别出我们日常生活中常见的各种物品。
|
||||
|
||||
“快速定制”新技能: 现在,我们想让这个AI“教授”学会一个新任务,比如区分“苹果”和“香蕉”。我们不需要让它从头开始学习,那样太慢了!
|
||||
|
||||
聪明做法: 我们直接“借用”MobileNet这个“教授”最擅长识别特征的“头部”(就像它最强大、最敏锐的“眼睛”和“大脑前部”),让它帮忙将你上传的“苹果”和“香蕉”图片,转化为它能理解的“特征描述”(比如“这是圆形、红色、有把手”、“这是长条形、黄色、弯曲的”)。
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们只需要给这些特征描述后面再添加一个非常简单的“小助理”模型,由它来学习和记住这些特征分别代表“苹果”还是“香蕉”就行了!
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们要从头开始训练一个图像分类模型,那么对于每个类我们需要成百上千张图片,并且使用专业的机器训练数小时甚至数天。这是一个耗时且昂贵的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
而迁移学习则可以让我们“借用”一个已经训练好的模型,只需要少量的新数据就可以训练出一个准确的模型。这大大节省了时间和金钱。
|
||||
|
||||
这里我们使用了mobilenet的预训练模型,其学习过上千中物品的特征,能够准确地识别出物品。因此我们使用这个预训练模型的头部作为特征检测器,它能够识别1000种它见过的物品。现在它观察一种新的物品时,就会给出1000个其见过物品的概率,我们只需要在后部再添加一个简单的分类模型,就可以快速实现分类了。
|
||||
|
||||
我们只需要训练少量的新数据,就可以训练出一个准确的模型。这就是迁移学习的魔力所在!
|
||||
|
||||
这样,我们的AI就能:
|
||||
|
||||
+ 只需要少量的新数据(几张图片!),
|
||||
+ 在短短几秒钟内,就能训练出一个准确的图片分类模型!
|
||||
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-29-43.mp4
Normal file
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-29-43.mp4
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-31-23.mp4
Normal file
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-31-23.mp4
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-32-27.mp4
Normal file
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-32-27.mp4
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-33-40.mp4
Normal file
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-33-40.mp4
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-35-32.png
Normal file
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-35-32.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 684 KiB |
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-37-34.png
Normal file
BIN
doc/姿态分类/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-37-34.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 838 KiB |
113
doc/姿态分类/README.md
Normal file
113
doc/姿态分类/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
## AI身体语言大师:你的酷炫姿态识别挑战! 🤸♀️🧘♂️
|
||||
> 核心概念: 姿态检测、人体关键点、机器学习、KNN分类、实时互动、可视化
|
||||
|
||||
### 开篇:AI也能“读懂”你的动作?——姿态分类模型怎么“看”身体语言?
|
||||
|
||||
嘿,未来科技探索者们!你有没有想过,手机上的健身App是如何判断你深蹲是否标准的?舞蹈游戏又是如何给你打分的?这可不是什么魔术,而是今天我们将一起揭秘的——人工智能(AI) 如何“看懂”我们的身体动作!
|
||||
|
||||
想象一下,你和朋友玩“你画我猜”,你们需要通过各种姿势来表达词语。人类的大脑很擅长理解这些姿势。那AI呢?它也能像我们一样“读懂”你的身体语言吗?
|
||||
|
||||
答案是:能! 我们的AI姿态分类模型,就像一个“身体语言大师”,它的任务就是学会区分各种身体姿态,比如“站立”、“坐下”、“挥手”、“跳跃”,甚至是你自己创造的酷炫动作!
|
||||
|
||||
----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
### AI如何“看穿”你的身体——人体关键点与KNN分类!
|
||||
|
||||
你可能会好奇:“AI怎么知道我摆的是什么姿势呢?”
|
||||
|
||||
但它有自己的“秘密武器”——姿态检测模型!
|
||||
|
||||
+ “AI骨架”——人体关键点:
|
||||
想象你是一个木偶,身上有手肘、膝盖、肩膀、脚踝等可以弯曲和转动的关节。这些关节就是AI眼中的“人体关键点”!
|
||||
我们的网站使用了一个叫 MoveNet 的超强AI模型,它能实时从你的摄像头画面中,精准地“描绘”出你的身体骨架,定位出大约17个关键点的位置(比如你的左肩在哪里,右膝盖在哪里)。这些关键点就像一个个数字坐标,描述了你身体的形状。
|
||||
|
||||
+ “找相似”高手——KNN分类(K-近邻算法):
|
||||
现在,AI有了你的“骨架图”(一系列数字关键点)。那它怎么知道这副骨架代表的是“站立”还是“坐下”呢?
|
||||
这里就要用到另一个简单又聪明的AI算法——KNN分类(K-近邻算法)!
|
||||
|
||||
+ 它的原理很简单: 想象你有一群朋友,他们穿着不同的运动服(代表不同的姿态类别)。当你摆出一个新姿势时,KNN就会问:“这个新姿势,跟我的哪几个朋友最像呢?”
|
||||
|
||||
+ 它会测量你新姿势的“骨架数据”,和所有它已经“认识”的姿势数据进行比较。哪个姿势跟你的“形状”最接近,AI就判断你当前摆的就是那个姿势!
|
||||
这样,我们的AI就能:
|
||||
|
||||
实时捕捉你的身体骨架!
|
||||
通过“找朋友”的方式,快速判断你摆的是什么姿势!
|
||||
是不是超酷?我们的可视化网站就是帮你亲手体验这个AI“身体语言大师”的神奇力量!
|
||||
|
||||
亲手打造你的AI“身体语言大师”!——尝试一下!
|
||||
现在,就让我们打开你的“AI训练营”网站,亲手“教”AI识别你的姿态吧!
|
||||
|
||||
[]
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤一:创建你的专属“姿态词典”——动态添加姿态类别!
|
||||
|
||||
在网站的“控制面板”区域,你会看到一个“+ 增加分类”按钮。点击它!
|
||||
会出现一个新分类,比如叫“Class 1”。你可以点击输入框,把它改成你喜欢的名字,比如“站立”、“蹲下”、“举手礼”、“瑜伽A式”等。
|
||||
💡 小贴士: 你可以多创建几个类别,比如“左手举起”、“右手举起”、“双手高举”,看看AI能不能区分这些细微的差别!
|
||||
### 步骤二:录入你的“姿态样本”——教AI认识你的动作!
|
||||
|
||||
这是最关键的一步!让AI看你的动作,记住你的“骨架数据”。
|
||||
|
||||
选择一个类别: 比如你创建了“站立”这个类别。
|
||||
摆好姿势: 面对摄像头,摆出你想要教AI的“站立”姿势。
|
||||
|
||||
### 点击“自动采集”或“采集样本”:
|
||||
“采集样本”: 每点击一次按钮,AI就会记录你当前的一个姿势样本。
|
||||
✨ 推荐使用“自动采集”: 点击它后,AI会在短短几秒内,自动、高效率地为你记录下10个姿势样本!这样你就不用一直按按钮啦!
|
||||
💡 小贴士: 采集样本时,姿势要标准,但也可以稍微有轻微的晃动,这有助于AI更好地学习这个姿势的“精髓”!
|
||||
为每个类别都采集足够的样本: 就像你考试前多做练习题一样,样本越多,AI就学得越准!每个类别至少采集10个以上样本会比较理想。
|
||||
更新UI: 你会看到每个类别旁边显示着“(X 样本)”,数字会随着你的采集而增加。
|
||||
步骤三:点击“开始预测”——看看AI是不是你的“身体语言大师”!
|
||||
|
||||
当所有姿态类别都采集完样本后,你就可以开始检测了!
|
||||
|
||||
点击“开始预测”按钮。
|
||||
现在,你再面对摄像头摆出你教过的姿态,AI会立刻告诉你,它觉得你摆的是哪个姿态,还会告诉你它有多大的把握(比如“姿态:站立 (95%)”)。
|
||||
哇塞!是不是超酷?你的AI现在也能“看懂”你的身体语言了!
|
||||
|
||||
<video controls src="https://goood-space-assets.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/public/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-29-43.mp4" title="Title"></video>
|
||||
<video controls src="https://goood-space-assets.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/public/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-31-23.mp4" title="Title"></video>
|
||||
<video controls src="https://goood-space-assets.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/public/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-32-27.mp4" title="Title"></video>
|
||||
<video controls src="https://goood-space-assets.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/public/PixPin_2025-08-22_14-33-40.mp4" title="Title"></video>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
玩了几轮之后,你可能会有更多的问题和想法,这正是一个AI探索家的开始!
|
||||
|
||||
如果AI判断错了怎么办?
|
||||
|
||||
这可能意味着你需要给AI采集更多的样本,或者你的训练样本和测试时的姿势不够一致。
|
||||
试试看: 重新选择判断错误的类别,再多采集一些样本,特别是那些AI容易混淆的类似姿势的样本!
|
||||
姿势样本数量越多越好吗?
|
||||
|
||||
思考题: 如果我只为每个姿态采集一个样本,AI能学会吗?(答案:很难!就像你只看了一个标准动作,就想教别人跳舞一样难!)
|
||||
你可以尝试: 分别用少量(比如每个类别3-5个)和大量(比如每个类别20-30个)样本训练AI,对比一下它们的识别准确率!你会发现一个有趣的规律!
|
||||
AI还能“读懂”什么?—— 拓展你的AI想象力!
|
||||
|
||||
展望: 你觉得这种姿态识别技术还能用在哪里?比如,智能健身镜纠正你的动作?游戏中的体感交互?老年人摔倒检测?AI辅助康复训练?
|
||||
集思广益: 想象一下,AI还能帮你解决什么问题?比如,识别你打篮球时的投篮姿势是否标准?识别手语动作?发挥你的创意,分享给你的小伙伴!未来属于你,AI的边界由你定义!
|
||||
进阶挑战:保存和加载你的AI“身体记忆”! (模型导入/导出)
|
||||
你有没有辛辛苦苦训练好一个AI,结果关掉网页就都没了的经历?别担心!我们的网站还提供了模型导入/导出功能,让你的AI“身体记忆”永不丢失!
|
||||
|
||||
“导出模型”: 训练好模型后,点击“导出模型”按钮,你的AI“身体记忆”(包含所有姿态类别和样本数据)就会保存为一个JSON文件下载到你的电脑里。
|
||||
“导入模型”: 下次你再打开网站,或者和朋友分享你的酷炫模型时,点击“导入模型”,选择你之前保存的JSON文件,你的AI就会立刻“恢复记忆”,知道你教过它的所有姿态了!
|
||||
恭喜你!你就是未来的AI创造者! ✨
|
||||
通过这个酷炫的可视化网站,你已经亲身体验了AI是如何:
|
||||
|
||||
“描绘”出你的身体骨架(姿态检测)!
|
||||
通过“找朋友”的方式学会识别不同姿态(KNN分类)!
|
||||
使用“超级加速器”(无需从零训练,因为我们用的MoveNet已经很聪明了!)实现快速学习!
|
||||
亲手塑造一个能“看懂”你身体语言的AI!
|
||||
这只是人工智能世界的一小部分精彩!未来,AI会融入我们生活的方方面面。而你,作为新一代的青少年,正是未来AI的创造者和使用者!保持好奇心,继续探索,也许下一个改变世界的AI应用,就出自你手!
|
||||
|
||||
祝你AI探秘之旅,姿态无限! 🌟
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
135
doc/音频检测/README.md
Normal file
135
doc/音频检测/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## **AI听力超能力:你的智能语音助手训练营!** 👂🎤
|
||||
|
||||
> **核心概念:** 迁移学习、声音分类、音频识别、机器学习、实时互动
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### **开篇:AI也能“听懂”悄悄话?——声音分类模型怎么“听”世界?**
|
||||
|
||||
嘿,未来科技探索者们!
|
||||
你有没有对着智能音箱说“播放音乐”,它就能立刻响应?或者手机上的App能识别你哼唱的歌曲?这些“耳朵超灵敏”的AI可不是魔法,而是今天我们将一起揭秘的——**人工智能(AI)** 如何“听懂”我们的声音世界!
|
||||
|
||||
想象一下,你第一次听到“猫”的叫声(喵呜~),“狗”的叫声(汪汪~),慢慢地,你就知道这两种声音代表不同的动物了。你的大脑在听到声音后,能分辨出它们的音高、音色、节奏等特点,并和记忆中的声音进行匹配。
|
||||
|
||||
**AI也是一样!** 但它需要大量的声音样本来学习。我们的AI**声音分类模型**,就像一个“听音辨声大师”,它的任务就是通过学习海量音频,学会区分不同类型的声音,比如“拍手声”、“风声”、“人说话声”,甚至是你的口令词!
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### **大揭秘:AI如何“捕捉”声音的秘密——音频特征与迁移学习!**
|
||||
|
||||
你可能会问:“声音那么复杂,AI怎么知道我在说什么,或者发出了什么声音呢?”
|
||||
|
||||
AI确实没有耳朵,但它有自己的“秘密武器”——**音频分析和机器学习**!
|
||||
|
||||
1. **“AI耳朵”——声音特征提取:**
|
||||
当声音进入麦克风,它会变成一串复杂的数字信号。我们的AI会用一种特殊的“魔法”,把这些数字信号变成一张张图片——我们称之为**“声谱图”**(Specgram)。声谱图就像是声音的“指纹”,它用颜色和图案,形象地展示了声音的音高、响度、持续时间等信息。
|
||||
AI识别声音,就像识别这些“声谱图”一样,它从中找出独特的模式,比如拍手声可能有一个快速、高亮的图案,而风声则可能是连续、低沉的模糊图案。
|
||||
|
||||
2. **“超级加速器”——迁移学习(声学版)!**
|
||||
还记得我们之前说的“迁移学习”吗?在声音领域,它依然是个超级英雄!
|
||||
如果你让AI从零开始学习各种声音,那它得听几百万小时的噪音和语音,才能学会区分最基础的“人声”和“环境音”。这太慢了!
|
||||
**我们用的方法是:** 借用一个已经很聪明的AI“听音教授”——它已经“听”了数不清的音频,学会了识别各种基本的声音特征(比如噪音是什么样的,短暂的敲击声是什么样的)。
|
||||
* **我们的秘诀就是:** **Speech Commands 模型**!这个模型已经预先学习了上千种日常声音和口令词。它就像一个拥有“顺风耳”的AI侦探👂,能从复杂的音频中捕捉到最关键的“声音指纹”。
|
||||
* **它的“超级大脑”里已经内置了对“背景噪音”(`_background_noise_`)的理解!** 这意味着它已经知道,那些杂乱无章、没有特定意义的声音长什么样。所以,我们最重要的一步就是先教它识别你所处的“背景噪音”——这样它就能把你的目标声音和周围的环境音区分开来。
|
||||
* 然后,我们只需要给它播放少量你想要识别的**特定声音样本**(比如“拍手”,或你自己说的“开始”),它就能在这个“教授”的基础上,非常快速地学会区分这些新声音!
|
||||
|
||||
3. **“找朋友”高手——KNN分类(K-近邻算法):**
|
||||
和姿态分类一样,AI在提取出声音的“特征指纹”后,就会用KNN算法来“找朋友”。它会将你当前听到的声音指纹,与它学过的所有声音指纹进行比较,哪个声音指纹“最像”,它就认为当前听到的是那种声音!
|
||||
|
||||
**这样,我们的AI就能:**
|
||||
|
||||
* **智能过滤环境杂音(通过背景噪音学习)!**
|
||||
* **快速学会并识别你的自定义声音!**
|
||||
|
||||
是不是超酷?我们的可视化网站就是帮你亲手体验这个AI“听音辨声大师”的神奇力量!
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### **亲手打造你的AI“听音辨声大师”!——尝试一下!**
|
||||
|
||||
现在,就让我们打开你的“AI训练营”网站,亲手“教”AI识别你的声音吧!
|
||||
[预留图片页面]
|
||||
在页面上,你会看到几个主要区域:**状态信息**、**背景噪音录制**、**自定义类别管理**、**模型控制**和**预测结果显示**。
|
||||
|
||||
**步骤一:🤫 录制背景噪音——教AI听清你的声音!**
|
||||
|
||||
这是非常关键的第一步!为了让AI更好地识别你想要的目标声音,它需要先知道你所处环境的“无意义”声音是怎样的。
|
||||
|
||||
* 找到“**🤫 1. 录制背景噪音**”区域。
|
||||
* 保持周围环境安静,没有你想要识别的特定声音。
|
||||
* 点击“**录制样本**”按钮(背景噪音的按钮通常是红色或特别标记的)。
|
||||
* AI会自动为你录制几段背景噪音。你会看到“样本数量”在增加。
|
||||
* **💡 小贴士:** 确保录制时不要发出你打算训练的目标声音!多录制一些(比如 5-10 个)效果会更好!
|
||||
|
||||
**步骤二:🗣️ 录制你想要分类的声音——创建你的“声音字典”!**
|
||||
|
||||
现在,是时候教AI认识你自己的声音了!
|
||||
|
||||
* **添加新类别:** 在“**🗣️ 2. 录制您要分类的声音**”下方的输入框中,输入你想要识别的声音的名称(比如“拍手”、“吹口哨”、“开始”、“停止”)。然后点击“**添加类别**”按钮。
|
||||
* 你会看到一个专属的类别块出现,里面有“样本数量”和“录制样本”按钮。
|
||||
* **为每个类别录制样本:**
|
||||
* 选择一个你刚创建的类别。
|
||||
* 每次点击“**录制样本**”按钮,就发出那个声音一次。例如,如果你创建了“拍手”类别,就对着麦克风拍一次手。
|
||||
* AI会自动帮你录制多段样本。你会看到对应类别的“样本数量”在增加。
|
||||
* **💡 小贴士:** 试着从不同强度、不同方式发出同一个声音,让AI学习到更丰富的特征!每个类别至少录制5-10个样本效果最好。
|
||||
* 重复以上步骤,添加并录制所有你想要识别的声音类别!
|
||||
|
||||
**步骤三:🚀 训练模型——让AI“融会贯通”!**
|
||||
|
||||
当你为所有类别(包括背景噪音)都录制了足够的样本后,就可以让AI开始学习了。
|
||||
|
||||
* 点击“**🚀 3. 训练模型**”按钮。
|
||||
* 你会看到“状态”区域显示模型的训练进度(例如“训练 Epoch 1/50”)。这个过程可能需要一些时间,取决于你的样本数量和网络速度。
|
||||
* **耐心等待:** 当“状态”显示“模型训练完成!”时,恭喜你,你的AI已经学成了!
|
||||
|
||||
**步骤四:👂 开始识别——看看你的AI有多强!**
|
||||
|
||||
现在,是检验成果的时候了!
|
||||
|
||||
* 点击“**👂 4. 开始识别**”按钮。
|
||||
* 对着麦克风发出你训练过的声音,或者只是保持安静(让它识别背景噪音)。
|
||||
* AI会立刻告诉你,它听到了什么声音,还会告诉你它有多大的把握(例如:“预测结果:拍手 (置信度: 98%)”)。
|
||||
* **哇塞!是不是超酷?你的AI现在也能“听懂”你的指令了!**
|
||||
* 当你玩够了,点击“**⏸️ 停止识别**”按钮,就可以暂停识别了。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### **挑战你的AI!—— 成为AI“声音训练专家”!**
|
||||
|
||||
玩了几轮之后,你可能会有更多的问题和想法,这正是一个AI探索家的开始!
|
||||
|
||||
* **如果AI判断错了怎么办?**
|
||||
* 这可能意味着你需要给AI采集更多的样本,或者你的样本不够清晰、不够多样。
|
||||
* **试试看:** 重新选择判断错误的类别,再多采集一些样本,特别是那些AI容易混淆的类似声音的样本!
|
||||
|
||||
* **声音样本数量越多越好吗?**
|
||||
* **思考题:** 如果我只为每个声音采集一个样本,AI能学会吗?(答案:很难!就像你只听过一次课就想考满分一样难!AI需要多听多练才能成为专家。)
|
||||
* **你可以尝试:** 分别用少量(比如每个类别3-5个)和大量(比如每个类别20-30个)样本训练AI,对比一下它们的识别准确率!你会发现一个有趣的规律!
|
||||
|
||||
* **AI还能“听懂”什么?—— 拓展你的AI想象力!**
|
||||
* **展望:** 你觉得这种声音识别技术还能用在哪里?比如,识别家里的电器开关声?宠物叫声的识别?婴儿啼哭声的分析?智能安防系统识别异常声音(玻璃破碎、警报)?
|
||||
* **集思广益:** 想象一下,AI还能帮你解决什么问题?发挥你的创意,分享给你的小伙伴!**未来属于你,AI的边界由你定义!**
|
||||
|
||||
### **进阶挑战:保存和加载你的AI“声音记忆”! (数据导入/导出)**
|
||||
|
||||
你有没有辛辛苦苦训练好一个AI,结果关掉网页就都没了的经历?别担心!我们的网站还提供了模型导入/导出功能,让你的AI“声音记忆”永不丢失!
|
||||
|
||||
* **“💾 导出数据”:** 训练好模型后,点击“导出数据”按钮,你的AI“声音记忆”(包含所有声音类别和样本数据)就会保存为一个`.bin`文件下载到你的电脑里。
|
||||
* **“📂 导入数据”:** 下次你再打开网站,或者和朋友分享你的酷炫模型时,点击“导入数据”,选择你之前保存的`.bin`文件,你的AI就会立刻“恢复记忆”,知道你教过它的所有声音了!
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### **恭喜你!你就是未来的AI创造者!** ✨
|
||||
|
||||
通过这个酷炫的可视化网站,你已经亲身体验了AI是如何:
|
||||
|
||||
* **“听”取声音并提取特征(通过声谱图)!**
|
||||
* **智能过滤环境噪音(通过背景噪音学习)!**
|
||||
* **快速学会并识别你的各种自定义声音(音频迁移学习和KNN分类)!**
|
||||
* 亲手塑造一个能“听懂”你声音的AI!
|
||||
|
||||
这只是人工智能世界的一小部分精彩!未来,AI会融入我们生活的方方面面。而你,作为新一代的青少年,正是未来AI的创造者和使用者!保持好奇心,继续探索,也许下一个改变世界的AI应用,就出自你手!
|
||||
|
||||
**祝你AI探秘之旅,声音无限!** 🔊
|
||||
40
game/分类器/arduino.ino
Normal file
40
game/分类器/arduino.ino
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
#include <Servo.h> // 加载舵机库
|
||||
Servo myservo; // 创建舵机对象
|
||||
|
||||
void setup() {
|
||||
myservo.attach(9); // 将舵机信号线连接到数字9引脚
|
||||
Serial.begin(9600);// 初始化串口,设置波特率为9600
|
||||
// myservo.write(0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop() {
|
||||
for (int pos = 80; pos <= 100; pos += 1) { // 从0°转到180°
|
||||
myservo.write(pos); // 设置舵机角度
|
||||
delay(15); // 等待15毫秒
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int pos = 100; pos >= 80; pos -= 1) {
|
||||
myservo.write(pos); // 设置舵机角度
|
||||
delay(15); // 等待15毫秒
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
|
||||
// 读取数据
|
||||
char received = Serial.read();
|
||||
// 输出数据
|
||||
Serial.print("Received: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(received);
|
||||
|
||||
if (received == '1'){
|
||||
myservo.write(0);
|
||||
for ( int i = 0;i <= 100;i += 1){
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (received == '2') {
|
||||
myservo.write(180);
|
||||
for ( int i = 0;i <= 100;i += 1){
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
53
game/分类器/index.html
Normal file
53
game/分类器/index.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="zh-CN">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="UTF-8">
|
||||
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
|
||||
<title>Web Serial KNN Classifier</title>
|
||||
<!-- TensorFlow.js 核心库 -->
|
||||
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow/tfjs@latest"></script>
|
||||
<!-- MobileNet 模型 -->
|
||||
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow-models/mobilenet@latest"></script>
|
||||
<!-- KNN 分类器 -->
|
||||
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow-models/knn-classifier@latest"></script>
|
||||
<style>
|
||||
body { font-family: sans-serif; margin: 20px; text-align: center; background-color: #f0f0f0; }
|
||||
h1 { color: #333; }
|
||||
.container { max-width: 800px; margin: 20px auto; padding: 20px; background-color: white; border-radius: 8px; box-shadow: 0 4px 10px rgba(0,0,0,0.1); }
|
||||
video { width: 100%; max-width: 640px; border: 1px solid #ccc; background-color: black; margin-top: 15px; border-radius: 4px;}
|
||||
button { padding: 10px 20px; font-size: 16px; margin: 5px; cursor: pointer; border: none; border-radius: 4px; transition: background-color 0.3s; }
|
||||
button:hover:not(:disabled) { background-color: #007bff; color: white; }
|
||||
button:disabled { background-color: #ccc; cursor: not-allowed; }
|
||||
.status-message { margin-top: 15px; padding: 10px; border-radius: 4px; }
|
||||
.status-info { background-color: #e0f7fa; color: #007bff; }
|
||||
.status-success { background-color: #e8f5e9; color: #4caf50; }
|
||||
.status-error { background-color: #ffebee; color: #f44336; }
|
||||
#prediction { font-size: 1.2em; font-weight: bold; margin-top: 20px; color: #333; }
|
||||
#serialStatus { margin-top: 10px; }
|
||||
</style>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<div class="container">
|
||||
<h1>📦 Web Serial 实时分类器</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
<div id="serialStatus" class="status-message status-info">正在检查 Web Serial API 兼容性...</div>
|
||||
<button id="connectSerialBtn" disabled>连接串口</button>
|
||||
<button id="disconnectSerialBtn" disabled>断开串口</button>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr style="margin: 20px 0;">
|
||||
|
||||
<div id="modelStatus" class="status-message status-info">正在加载 MobileNet 和 KNN 模型...</div>
|
||||
<button id="loadModelBtn">加载模型文件</button>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr style="margin: 20px 0;">
|
||||
|
||||
<button id="startWebcamBtn" disabled>启动摄像头</button>
|
||||
<button id="stopWebcamBtn" disabled>停止摄像头</button>
|
||||
<video id="webcam" autoplay playsinline muted></video>
|
||||
|
||||
<div id="prediction">等待识别...</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<script src="script.js"></script>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
BIN
game/分类器/models/knn-model.bin
Normal file
BIN
game/分类器/models/knn-model.bin
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
1
game/分类器/models/knn-model.json
Normal file
1
game/分类器/models/knn-model.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
{"dataset":{"0":{"start":0,"length":38400},"1":{"start":38400,"length":38400}},"classList":[{"id":"class-1","name":"Class 1","images":[]},{"id":"class-2","name":"Class 2","images":[]}],"k":3,"featureDim":1280,"date":"2025-08-24T02:07:00.303Z","dataFile":"knn-model.bin"}
|
||||
44
game/分类器/models/test.py
Normal file
44
game/分类器/models/test.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import json
|
||||
|
||||
json_file_path = './knn-model.json'
|
||||
bin_file_path = './knn-model.bin'
|
||||
|
||||
with open(json_file_path, 'r') as f:
|
||||
model_data = json.load(f)
|
||||
|
||||
with open(bin_file_path, 'rb') as f:
|
||||
binary_full_data = f.read()
|
||||
|
||||
feature_dim = model_data['featureDim']
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"Feature Dimension: {feature_dim}")
|
||||
|
||||
for label, meta in model_data['dataset'].items():
|
||||
start_byte = meta['start']
|
||||
length_byte = meta['length']
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"\n--- Class: {label} ---")
|
||||
print(f"Start Byte: {start_byte}")
|
||||
print(f"Length Byte: {length_byte}")
|
||||
|
||||
# 提取当前类别的数据片段
|
||||
class_binary_data = binary_full_data[start_byte : start_byte + length_byte]
|
||||
|
||||
# 转换为 Float32 数组
|
||||
try:
|
||||
class_features_elements = np.frombuffer(class_binary_data, dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
num_elements = len(class_features_elements)
|
||||
print(f"Float32 elements extracted: {num_elements}")
|
||||
|
||||
if num_elements % feature_dim == 0:
|
||||
num_samples = num_elements // feature_dim
|
||||
print(f"SUCCESS: Aligned. Number of samples: {num_samples}")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(f"ERROR: Not aligned. {num_elements} elements / {feature_dim} dim = {num_elements / feature_dim} (not an integer).")
|
||||
print(f"Expected length in bytes to be multiple of {feature_dim * 4} = {feature_dim * 4} bytes.")
|
||||
print(f"Actual length in bytes: {length_byte}. Remainder when dividing by {feature_dim * 4}: {length_byte % (feature_dim * 4)}")
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"Error processing binary data for class {label}: {e}")
|
||||
|
||||
604
game/分类器/script.js
Normal file
604
game/分类器/script.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,604 @@
|
||||
// script.js
|
||||
|
||||
const VIDEO = document.getElementById('webcam');
|
||||
const CONNECT_SERIAL_BTN = document.getElementById('connectSerialBtn');
|
||||
const DISCONNECT_SERIAL_BTN = document.getElementById('disconnectSerialBtn');
|
||||
const LOAD_MODEL_BTN = document.getElementById('loadModelBtn');
|
||||
const START_WEBCAM_BTN = document.getElementById('startWebcamBtn');
|
||||
const STOP_WEBCAM_BTN = document.getElementById('stopWebcamBtn');
|
||||
const MODEL_STATUS = document.getElementById('modelStatus');
|
||||
const SERIAL_STATUS = document.getElementById('serialStatus');
|
||||
const PREDICTION_OUTPUT = document.getElementById('prediction');
|
||||
|
||||
let mobilenet; // 这个变量将存储加载后的 MobileNet 模型实例
|
||||
let knnClassifier; // 这个变量将存储 KNN 分类器实例
|
||||
let classNames = []; // 类别名称将从加载的模型中获取
|
||||
let webcamStream = null;
|
||||
let isPredicting = false;
|
||||
|
||||
// Web Serial API 变量
|
||||
let serialPort = null;
|
||||
let serialWriter = null;
|
||||
const SERIAL_BAUD_RATE = 9600;
|
||||
const SERIAL_SEND_MIN_INTERVAL = 500; // 最短发送间隔,500ms,用于内部节流
|
||||
let lastSerialCommand = ''; // 用于sendToSerialPort内部的节流(避免重复命令+短间隔)
|
||||
let lastSerialSendTime = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
// 新增变量:追踪串口连接状态,并记录上一次发送到串口的类别命令
|
||||
let isSerialConnectedState = false; // 跟踪串口的逻辑连接状态
|
||||
let lastSentClassCommand = null; // 上一次"成功通过确认机制并实际发送"的命令
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
// 新增变量:用于实现“确认式”发送逻辑
|
||||
let pendingCommandToSend = null; // 正在等待确认的命令
|
||||
let pendingCommandTimerId = null; // 确认定时器ID
|
||||
const CONFIRMATION_DELAY_MS = 100; // 等待 100 毫秒确认 class 是否稳定
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
// Helper Functions (UI Status)
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
function showStatus(element, type, message) {
|
||||
element.className = `status-message status-${type}`;
|
||||
element.textContent = message;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function updateSerialUI(isConnected) {
|
||||
CONNECT_SERIAL_BTN.disabled = isConnected;
|
||||
DISCONNECT_SERIAL_BTN.disabled = !isConnected;
|
||||
isSerialConnectedState = isConnected; // 更新我们维护的串口连接状态
|
||||
if (!isConnected) {
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'info', '串口未连接。点击 "连接串口" 开始。');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function updateWebcamUI(isRunning) {
|
||||
START_WEBCAM_BTN.disabled = isRunning;
|
||||
STOP_WEBCAM_BTN.disabled = !isRunning;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function updateModelUI(isLoaded) {
|
||||
LOAD_MODEL_BTN.disabled = false; // 总是允许重新加载模型
|
||||
START_WEBCAM_BTN.disabled = !isLoaded; // 模型加载后才能启动摄像头
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
// Core Logic: Model & Webcam
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
async function initModel() {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'info', '正在加载 MobileNet 模型...');
|
||||
try {
|
||||
mobilenet = await window.mobilenet.load({ version: 2, alpha: 1.0 });
|
||||
knnClassifier = window.knnClassifier.create();
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'success', 'MobileNet 模型和 KNN 分类器已加载。请加载模型文件。');
|
||||
updateModelUI(false); // 此时 MobileNet 已加载,但 KNN 分类器本身还需加载数据
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'error', `模型加载失败: ${error.message}`);
|
||||
console.error('MobileNet/KNN加载失败:', error);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 提取 MobileNet 特征
|
||||
async function getFeatures(img) {
|
||||
if (!mobilenet) {
|
||||
throw new Error("MobileNet model is not loaded.");
|
||||
}
|
||||
return tf.tidy(() => {
|
||||
const embeddings = mobilenet.infer(img, true);
|
||||
const norm = tf.norm(embeddings);
|
||||
const normalized = tf.div(embeddings, norm);
|
||||
return normalized;
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 加载 KNN 模型文件,支持 '.json' 和 '.bin' 两部分文件。
|
||||
* 用户需要依次选择对应的 .json 和 .bin 文件。
|
||||
*/
|
||||
async function loadKNNModel() {
|
||||
const inputJson = document.createElement('input');
|
||||
inputJson.type = 'file';
|
||||
inputJson.accept = '.json';
|
||||
inputJson.multiple = false;
|
||||
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'info', '请先选择 KNN 模型配置文件 (.json)...');
|
||||
|
||||
inputJson.onchange = async (e) => {
|
||||
const jsonFile = e.target.files[0];
|
||||
if (!jsonFile) {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'info', '未选择 .json 文件。');
|
||||
updateModelUI(false);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'info', `正在解析 ${jsonFile.name}...`);
|
||||
|
||||
let modelData;
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const reader = new FileReader();
|
||||
const jsonText = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
reader.onload = () => resolve(reader.result);
|
||||
reader.onerror = () => reject(reader.error);
|
||||
reader.readAsText(jsonFile);
|
||||
});
|
||||
modelData = JSON.parse(jsonText);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!modelData.dataFile) {
|
||||
console.warn('模型JSON文件不包含 "dataFile" 字段,尝试以旧的单文件JSON格式加载。');
|
||||
return loadSingleJsonModel(modelData);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'error', `解析 .json 文件失败: ${error.message}`);
|
||||
console.error('解析 .json 失败:', error);
|
||||
updateModelUI(false);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const inputBin = document.createElement('input');
|
||||
inputBin.type = 'file';
|
||||
inputBin.accept = '.bin';
|
||||
inputBin.multiple = false;
|
||||
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'info', `已加载 .json 文件。请选择对应的权重文件 "${modelData.dataFile}" (.bin)...`);
|
||||
|
||||
inputBin.onchange = async (eBin) => {
|
||||
const binFile = eBin.target.files[0];
|
||||
if (!binFile) {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'info', '未选择 .bin 文件。');
|
||||
updateModelUI(false);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (binFile.name !== modelData.dataFile) {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'error', `选择的 .bin 文件名 "${binFile.name}" 与 .json 中定义的 "${modelData.dataFile}" 不匹配!请选择正确的文件。`);
|
||||
updateModelUI(false);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'info', `正在读取 ${binFile.name} (二进制权重文件)...`);
|
||||
let binData;
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const reader = new FileReader();
|
||||
const arrayBuffer = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
||||
reader.onload = () => resolve(reader.result);
|
||||
reader.onerror = () => reject(reader.error);
|
||||
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(binFile);
|
||||
});
|
||||
binData = new Float32Array(arrayBuffer);
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'error', `读取 .bin 文件失败: ${error.message}`);
|
||||
console.error('读取 .bin 失败:', error);
|
||||
updateModelUI(false);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
knnClassifier.clearAllClasses();
|
||||
|
||||
Object.keys(modelData.dataset).forEach(label => {
|
||||
const classDataMeta = modelData.dataset[label];
|
||||
const startFloat32ElementIndex = classDataMeta.start;
|
||||
const numFloat32Elements = classDataMeta.length;
|
||||
|
||||
const featureDim = modelData.featureDim || 1280;
|
||||
|
||||
const classFeatures = binData.subarray(startFloat32ElementIndex, startFloat32ElementIndex + numFloat32Elements);
|
||||
|
||||
if (classFeatures.length === 0) {
|
||||
console.warn(`类别 ${label} 没有找到特征数据,跳过。`);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (classFeatures.length % featureDim !== 0) {
|
||||
const actualSamples = classFeatures.length / featureDim;
|
||||
console.error(
|
||||
`--- 类别: ${label} ---`,
|
||||
`起始 Float32 元素索引: ${startFloat32ElementIndex}`,
|
||||
`该类别 Float32 元素数量: ${numFloat32Elements}`,
|
||||
`ERROR: 特征数据长度 (${classFeatures.length} 个 Float32 元素) 与特征维度 (${featureDim}) 不匹配!` +
|
||||
`实际样本数计算为 ${actualSamples} (预期为整数)。`,
|
||||
`请检查您的模型导出逻辑和训练数据的完整性。`
|
||||
);
|
||||
throw new Error("模型数据完整性错误:特征数据长度与维度不匹配。");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const numSamples = classFeatures.length / featureDim;
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < numSamples; i++) {
|
||||
const startIndex = i * featureDim;
|
||||
const endIndex = (i + 1) * featureDim;
|
||||
const sampleFeatures = classFeatures.subarray(startIndex, endIndex);
|
||||
|
||||
const sampleTensor = tf.tensor(sampleFeatures, [1, featureDim]);
|
||||
|
||||
knnClassifier.addExample(sampleTensor, parseInt(label));
|
||||
tf.dispose(sampleTensor);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
if (modelData.classList && Array.isArray(modelData.classList)) {
|
||||
classNames = modelData.classList.map(c => c.name);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
console.warn('模型JSON中未找到 classList 字段或格式不正确,使用默认类别名称。');
|
||||
classNames = Object.keys(modelData.dataset).map(key => `Class ${parseInt(key) + 1}`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'success', `模型 "${jsonFile.name}" 及权重加载成功!类别: ${classNames.join(', ')}。`);
|
||||
updateModelUI(true);
|
||||
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'error', `处理模型数据失败: ${error.message}`);
|
||||
console.error('处理模型数据失败:', error);
|
||||
updateModelUI(false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
inputBin.click();
|
||||
};
|
||||
inputJson.click();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 辅助函数:处理旧的单文件JSON模型格式( dataset 字段直接包含数据而不是偏移量)
|
||||
* @param {object} modelData - 已解析的 JSON 模型数据
|
||||
*/
|
||||
async function loadSingleJsonModel(modelData) {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
knnClassifier.clearAllClasses();
|
||||
Object.keys(modelData.dataset).forEach(key => {
|
||||
const data = modelData.dataset[key];
|
||||
const featureDim = modelData.featureDim || 1280;
|
||||
if (data.length % featureDim !== 0) {
|
||||
throw new Error(`类别 ${key} 的特征数据长度 ${data.length} 与特征维度 ${featureDim} 不匹配!`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
const numSamples = data.length / featureDim;
|
||||
const tensor = tf.tensor(data, [numSamples, featureDim]);
|
||||
knnClassifier.addExample(tensor, parseInt(key));
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
if (modelData.classList && Array.isArray(modelData.classList)) {
|
||||
classNames = modelData.classList.map(c => c.name);
|
||||
} else if (modelData.classNames && Array.isArray(modelData.classNames)) {
|
||||
classNames = modelData.classNames;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
console.warn('模型JSON中未找到 classList/classNames 字段,使用默认类别名称。');
|
||||
classNames = Object.keys(modelData.dataset).map(key => `Class ${parseInt(key) + 1}`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'success', `模型 (单文件JSON格式) 加载成功!类别: ${classNames.join(', ')}。`);
|
||||
updateModelUI(true);
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'error', `加载单文件JSON模型失败: ${error.message}`);
|
||||
console.error('加载单文件JSON模型失败:', error);
|
||||
updateModelUI(false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
async function startWebcam() {
|
||||
if (webcamStream) return;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!knnClassifier || knnClassifier.getNumClasses() === 0) {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'error', '请先加载训练好的模型!');
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const stream = await navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({ video: { facingMode: 'user' }, audio: false });
|
||||
VIDEO.srcObject = stream;
|
||||
webcamStream = stream;
|
||||
updateWebcamUI(true);
|
||||
|
||||
VIDEO.onloadeddata = () => {
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
// 启动摄像头时,重置所有发送状态,确保第一次识别结果可发送
|
||||
if (pendingCommandTimerId) {
|
||||
clearTimeout(pendingCommandTimerId);
|
||||
pendingCommandTimerId = null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
pendingCommandToSend = null;
|
||||
lastSentClassCommand = null;
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
isPredicting = true;
|
||||
predictLoop();
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'info', '摄像头已启动,开始实时预测...');
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'error', `无法访问摄像头: ${error.message}`);
|
||||
console.error('启动摄像头失败:', error);
|
||||
updateWebcamUI(false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function stopWebcam() {
|
||||
if (webcamStream) {
|
||||
webcamStream.getTracks().forEach(track => track.stop());
|
||||
webcamStream = null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
isPredicting = false;
|
||||
VIDEO.srcObject = null;
|
||||
updateWebcamUI(false);
|
||||
PREDICTION_OUTPUT.textContent = '等待识别...';
|
||||
showStatus(MODEL_STATUS, 'info', '摄像头已停止。');
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
// 停止摄像头时,清除任何待确认的命令,并发送“停止”或“复位”命令
|
||||
if (pendingCommandTimerId) {
|
||||
clearTimeout(pendingCommandTimerId);
|
||||
pendingCommandTimerId = null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
pendingCommandToSend = null;
|
||||
|
||||
// 假设 '0' 是停止/复位命令,并且只有当上次发送的不是 '0' 时才发送
|
||||
if (lastSentClassCommand !== '0') {
|
||||
sendToSerialPort('0');
|
||||
}
|
||||
lastSentClassCommand = null; // 重置,确保下次启动摄像头时能发送初始状态
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ============== 重要的修改区域 start ==============
|
||||
// 定义一个全局变量,用于存储当前帧识别到的命令,供 setTimeout 回调使用
|
||||
let currentCommandInFrame = '0'; // 初始值默认是 '0' (复位/无动作)
|
||||
|
||||
async function predictLoop() {
|
||||
if (!isPredicting) return;
|
||||
|
||||
if (VIDEO.readyState === 4 && VIDEO.videoWidth > 0 && VIDEO.videoHeight > 0) {
|
||||
let commandCandidate = '0'; // 每次循环开始时,将当前帧的候选命令初始化为'0'
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const features = await getFeatures(VIDEO);
|
||||
const k = 3;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!knnClassifier || knnClassifier.getNumClasses() === 0) {
|
||||
features.dispose();
|
||||
PREDICTION_OUTPUT.textContent = 'KNN 分类器未就绪或无数据。';
|
||||
commandCandidate = '0'; // 使用默认命令
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
const prediction = await knnClassifier.predictClass(features, k);
|
||||
features.dispose();
|
||||
|
||||
if (prediction && prediction.confidences) {
|
||||
let maxConfidence = 0;
|
||||
let predictedClassIndex = -1;
|
||||
|
||||
const confidencesArray = Object.entries(prediction.confidences).map(([key, value]) => ({ index: parseInt(key), confidence: value }));
|
||||
|
||||
confidencesArray.forEach(({ index, confidence }) => {
|
||||
if (confidence > maxConfidence) {
|
||||
maxConfidence = confidence;
|
||||
predictedClassIndex = index;
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const confidenceThreshold = 0.75; // 75%置信度
|
||||
if (predictedClassIndex !== -1 && maxConfidence > confidenceThreshold) {
|
||||
const className = classNames[predictedClassIndex] || `Class ${predictedClassIndex + 1}`;
|
||||
const percentage = (maxConfidence * 100).toFixed(1);
|
||||
PREDICTION_OUTPUT.textContent = `识别为: ${className} (${percentage}%)`;
|
||||
|
||||
// 根据类别设置本帧的候选命令
|
||||
if (predictedClassIndex === 0) {
|
||||
commandCandidate = '1';
|
||||
} else if (predictedClassIndex === 1) {
|
||||
commandCandidate = '2';
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
commandCandidate = '0'; // 未匹配到特定类别,或默认复位
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
PREDICTION_OUTPUT.textContent = `未知或不确定... (最高置信度: ${(maxConfidence * 100).toFixed(1)}%)`;
|
||||
commandCandidate = '0'; // 不确定也发送'0'回退
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
PREDICTION_OUTPUT.textContent = '无法识别。';
|
||||
commandCandidate = '0'; // 无法识别也发送 '0' 回退
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
console.error('预测错误:', error);
|
||||
PREDICTION_OUTPUT.textContent = `预测错误: ${error.message}`;
|
||||
commandCandidate = '0'; // 错误时也发送'0'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// =========================================================
|
||||
// 核心逻辑:确认式发送机制 (Persistence / Confirmation)
|
||||
// =========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
// 更新全局变量 currentCommandInFrame,指示当前帧的预测结果
|
||||
currentCommandInFrame = commandCandidate;
|
||||
|
||||
// 只有当当前帧的候选命令与上一次实际发送的命令不同时,才进入确认流程
|
||||
if (currentCommandInFrame !== lastSentClassCommand) {
|
||||
// 如果目前没有待确认的命令,或者待确认的命令与当前不同
|
||||
if (pendingCommandToSend === null || pendingCommandToSend !== currentCommandInFrame) {
|
||||
if (pendingCommandTimerId) {
|
||||
clearTimeout(pendingCommandTimerId); // 清除旧的等待定时器
|
||||
pendingCommandTimerId = null;
|
||||
// console.log(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] 命令在确认前再次变化,取消旧的确认定时器.`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pendingCommandToSend = currentCommandInFrame; // 设置新的待确认命令
|
||||
|
||||
// 设置一个定时器,在 CONFIRMATION_DELAY_MS 后进行确认
|
||||
pendingCommandTimerId = setTimeout(async () => {
|
||||
// 当定时器触发时,再次检查全局的 currentCommandInFrame
|
||||
// 如果它仍然与我们开始等待的命令相同,则确认并发送
|
||||
if (currentCommandInFrame === pendingCommandToSend) {
|
||||
console.log(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] 确认命令 "${pendingCommandToSend}" 稳定,正在发送。`);
|
||||
await sendToSerialPort(pendingCommandToSend);
|
||||
lastSentClassCommand = pendingCommandToSend; // 更新上一次实际发送的命令
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
console.log(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] 命令在确认期内再次变化 (${pendingCommandToSend} -> ${currentCommandInFrame}),不发送。`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
pendingCommandToSend = null; // 清理待确认状态
|
||||
pendingCommandTimerId = null; // 清理定时器ID
|
||||
}, CONFIRMATION_DELAY_MS);
|
||||
|
||||
// console.log(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] 检测到新候选命令 "${currentCommandInFrame}",启动 ${CONFIRMATION_DELAY_MS}ms 确认计时器。`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 如果 currentCommandInFrame 1. 仍然与 pendingCommandToSend 相同
|
||||
// 并且 2. 不同于 lastSentClassCommand
|
||||
// 说明它处在“正在等待确认”的状态,不需要做任何事情,让当前定时器继续运行
|
||||
} else { // 当前帧的命令与上次实际发送的命令相同
|
||||
// 如果已经发送了相同的命令,或者回到了已发送的命令,那么清除待确认定时器
|
||||
if (pendingCommandTimerId) {
|
||||
clearTimeout(pendingCommandTimerId);
|
||||
pendingCommandTimerId = null;
|
||||
pendingCommandToSend = null; // 清理待确认状态
|
||||
// console.log(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] 当前命令 "${currentCommandInFrame}" 与上次发送命令相同,或回摆,取消所有待确认发送。`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// =========================================================
|
||||
}
|
||||
requestAnimationFrame(predictLoop); // 继续下一帧预测
|
||||
}
|
||||
// ============== 重要的修改区域 end ==============
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
// Web Serial API Logic
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
async function checkWebSerialCompatibility() {
|
||||
if ('serial' in navigator) {
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'info', 'Web Serial API 可用!');
|
||||
CONNECT_SERIAL_BTN.disabled = false;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'error', 'Web Serial API 在此浏览器中不可用。请使用最新版 Chrome!');
|
||||
CONNECT_SERIAL_BTN.disabled = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
async function connectSerial() {
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'info', '正在请求连接串口...');
|
||||
try {
|
||||
serialPort = await navigator.serial.requestPort();
|
||||
|
||||
serialPort.addEventListener('disconnect', () => {
|
||||
const disconnectTime = new Date().toLocaleString();
|
||||
console.warn(`[${disconnectTime}] ❗️❗️❗️ 串口已断开连接事件触发! `); // 强调日志
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'error', '串口连接已丢失!');
|
||||
disconnectSerial();
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
await serialPort.open({ baudRate: SERIAL_BAUD_RATE });
|
||||
console.log('串口已成功打开。尝试获取写入器...');
|
||||
serialWriter = serialPort.writable.getWriter();
|
||||
console.log('写入器已获取。');
|
||||
|
||||
console.log('串口已连接并打开。');
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'success', `串口已连接 (Baud: ${SERIAL_BAUD_RATE})`);
|
||||
updateSerialUI(true); // 更新状态为已连接
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
console.error('连接串口失败:', error);
|
||||
if (error.name === 'NotFoundError') {
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'warning', '连接串口请求已取消或未选择端口。请选择一个设备。');
|
||||
} else if (error.name === 'SecurityError') {
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'error', `连接串口失败: ${error.message}。请确保您在安全上下文 (HTTPS 或 localhost) 中运行。`);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'error', `连接串口失败: ${error.message}`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
updateSerialUI(false); // 更新状态为未连接
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
async function disconnectSerial() {
|
||||
console.trace(`[${new Date().toLocaleString()}] disconnectSerial() called`);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!isSerialConnectedState && !serialPort && !serialWriter) {
|
||||
console.log('Already in disconnected state, skipping further cleanup.');
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
// 断开连接时,清除任何待确认的定时器和状态
|
||||
if (pendingCommandTimerId) {
|
||||
clearTimeout(pendingCommandTimerId);
|
||||
pendingCommandTimerId = null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
pendingCommandToSend = null;
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
if (serialWriter) {
|
||||
await serialWriter.close();
|
||||
serialWriter = null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (serialPort && serialPort.readable) {
|
||||
const reader = serialPort.readable.getReader();
|
||||
if (reader) {
|
||||
await reader.cancel();
|
||||
reader.releaseLock();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (serialPort && serialPort.isOpen) {
|
||||
await serialPort.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
serialPort = null;
|
||||
console.log('串口已断开。');
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'info', '串口已断开。');
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
console.error('断开串口失败或串口已处于非连接状态:', error);
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'error', `断开串口失败: ${error.message}`);
|
||||
} finally {
|
||||
updateSerialUI(false); // 无论如何都确保UI和状态更新为断开
|
||||
lastSentClassCommand = null; // 断开连接时,重置上一次发送的命令,确保重连后第一次变化能发送
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 低级串口发送函数。包含内部的频繁发送节流。
|
||||
* @param {string} command - 要发送的命令字符串。
|
||||
*/
|
||||
async function sendToSerialPort(command) {
|
||||
if (!isSerialConnectedState) {
|
||||
// console.warn('串口已断开(逻辑状态),无法发送命令。');
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!serialWriter) {
|
||||
console.warn(`[${new Date().toLocaleString()}] 串口连接状态为 true,但 serialWriter 不可用。尝试重置串口连接。`);
|
||||
disconnectSerial();
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 避免频繁发送相同的命令 (sendToSerialPort 内部的节流)
|
||||
const currentTime = new Date().getTime();
|
||||
if (command === lastSerialCommand && (currentTime - lastSerialSendTime < SERIAL_SEND_MIN_INTERVAL)) {
|
||||
return; // 命令相同且发送间隔太短,不发送
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const encoder = new TextEncoder();
|
||||
const data = encoder.encode(command + '\n');
|
||||
await serialWriter.write(data);
|
||||
console.log(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] 实际发送串口命令: ${command}`);
|
||||
lastSerialCommand = command; // 更新内部节流用的命令
|
||||
lastSerialSendTime = currentTime;
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
console.error(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] 实际发送串口命令失败: ${error.message}`);
|
||||
showStatus(SERIAL_STATUS, 'error', `发送串口命令失败: ${error.message},正在断开串口。`);
|
||||
disconnectSerial();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
// Event Listeners
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
CONNECT_SERIAL_BTN.addEventListener('click', connectSerial);
|
||||
DISCONNECT_SERIAL_BTN.addEventListener('click', disconnectSerial);
|
||||
LOAD_MODEL_BTN.addEventListener('click', loadKNNModel);
|
||||
START_WEBCAM_BTN.addEventListener('click', startWebcam);
|
||||
STOP_WEBCAM_BTN.addEventListener('click', stopWebcam);
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
// Initialization
|
||||
// ===================================
|
||||
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
|
||||
checkWebSerialCompatibility(); // 检查 Web Serial API 兼容性
|
||||
initModel(); // 加载 MobileNet 和 KNN 分类器实例
|
||||
});
|
||||
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user